


The tear film is a thin (2-6 µm) multi-layer fluid that coats the corneal and conjunctival epithelia. Its proximity to the ocular environment, coupled with the ease of its collection and rich protein content, makes it an attractive source for proteomic biomarker studies. Novel biomarker discoveries have the potential to offer valuable insights and enhance our understanding of various ocular diseases like dry eye disease, glaucoma, and blepharitis.
We have developed a Liquid-Chromatography /Mass spectrometry (LC-MS /MS) workflow for Data Independent Acquisition (DIA) proteomic analysis of tear fluid samples that has identified over 2000 unique proteins from human subjects. This method uses in-strip protein digestion of samples collected from Schirmer strips on an Orbitrap Fusion Tribrid mass spectrometer.
LC-MS/MS has emerged as the analytical method of choice because of its high -throughput nature, sensitivity, high dynamic range, and ability to identify complex mixtures even from small sample volumes. We plan to collect many tear samples using a standardized method and then develop a reference tear proteomic database to prioritize, integrate, and analyze potential DED biomarkers. We are prioritizing the collection of extensive clinical and demographic parameters that will allow for highly specific subject categorization and novel insights into various disease cohorts. This will provide a readily accessible and permanent resource, fostering collaboration between laboratories to expand and improve the database. This database will help the vision research community understand the physiological and pathological proteomic signatures in tear fluid.
Tear fluid collection is a simple and non-invasive process that can yield a high amount of information about the health of the body. To collect, each Schirmer strip is inserted into the lateral portion of the lower conjunctival sac of the eye for a period of five minutes. When the strip is gently inserted into the lower eyelid, individuals often compare the sensation to inserting a contact lens before closing their eyes for the duration of sample collection. As the eye remains closed, tear fluid and its valuable contents are absorbed and deposited onto the Schirmer strip that will be analyzed.
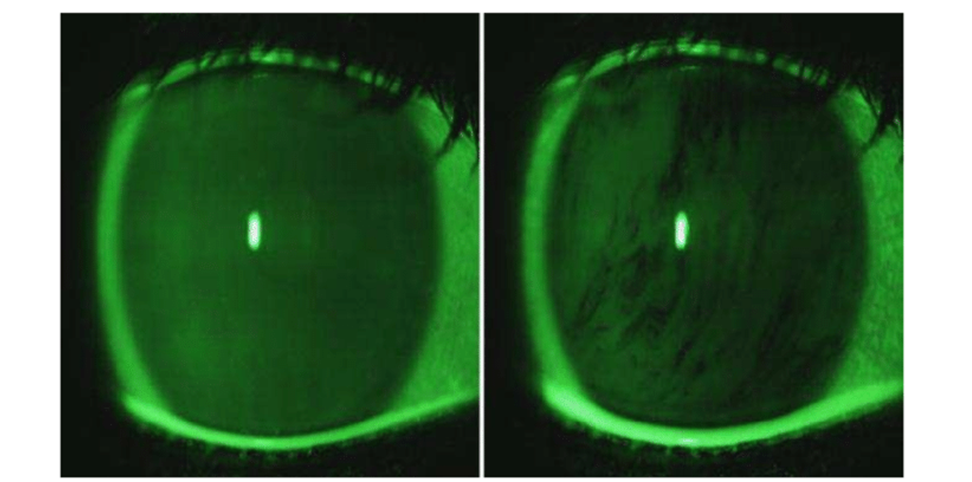
Disruption and abrasion of the corneal tissue
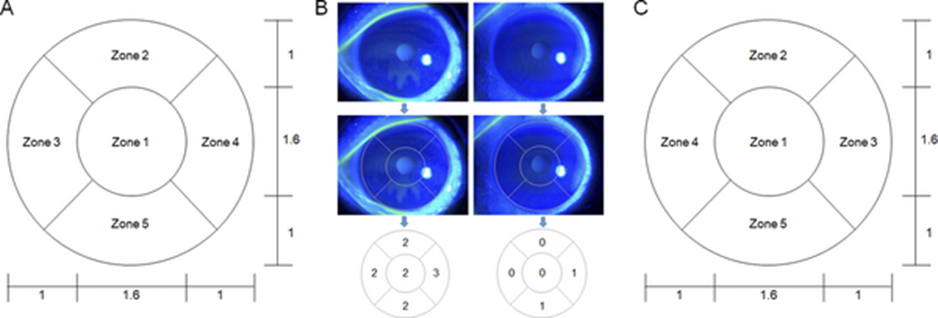
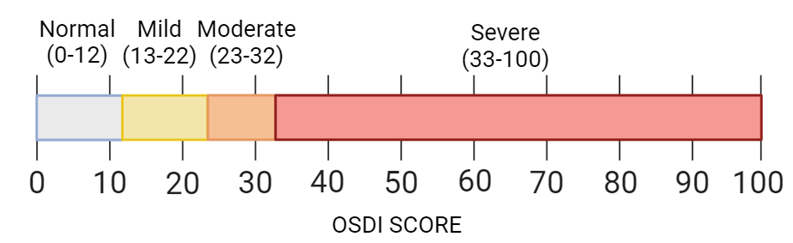
Measures the severity of dry eye disease
The amount of time it takes after blinking for the first formation of a dry spot
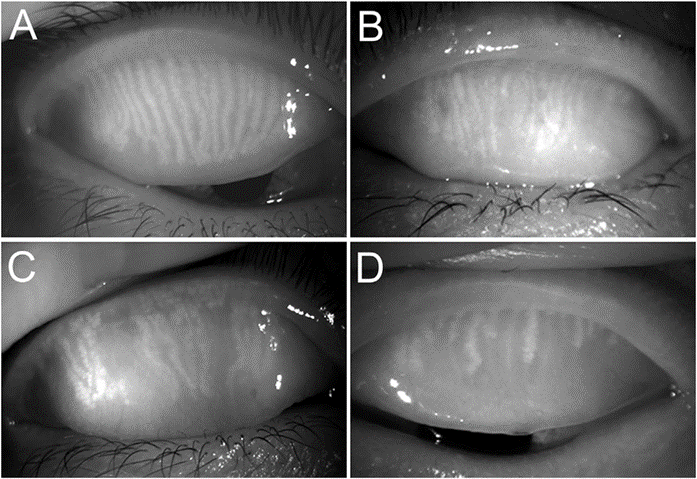
Indicator of the damage to the Meibomian Glands, which help to stabilize the tear film
These clinical parameters each affect tear film formation, and therefore its’ proteomic composition. Including these parameters encourages differential analysis on the proteomic composition of tear film under various stresses.
